3.6 KiB
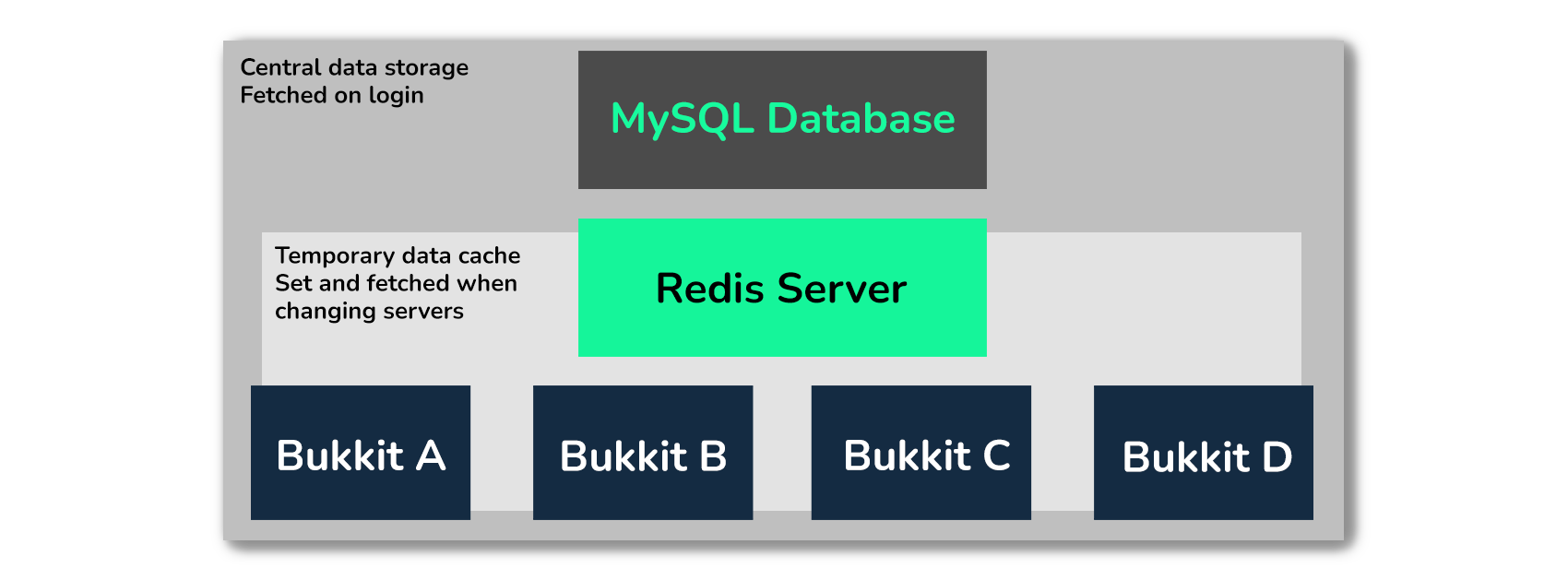
HuskSync offers two built-in synchronization modes that utilise Redis and MySQL to optimally sync data as users change servers (illustrated below). These sync modes change the way data is synced between servers, and can be changed in the config.yml file.
Available Modes
- The
LOCKSTEPsync mode is the default sync mode. It uses a data checkout system to ensure that all servers are in sync regardless of network latency or tick rate fluctuations. This mode was introduced in HuskSync v3.1 - The
DELAYsync mode uses thenetwork_latency_milisecondsvalue to apply a delay before listening to Redis data
You can change which sync mode you are using by editing the sync_mode setting under synchronization in config.yml.
Warning: Please note that you must use the same sync mode on all servers (at least within a cluster).
Changing the sync mode (config.yml)
synchronization:
# The data synchronization mode to use (LOCKSTEP or DELAY). LOCKSTEP is recommended for most networks. Docs: https://william278.net/docs/husksync/sync-modes
mode: LOCKSTEP
Lockstep
The LOCKSTEP sync mode works as described below:
- When a user connects to a server, the server will continuously asynchronously check if a
DATA_CHECKOUTkey is present.- If, or when, the key is not present, the plugin will set a new
DATA_CHECKOUTkey.
- If, or when, the key is not present, the plugin will set a new
- After this, the plugin will check Redis for the presence of a
DATA_UPDATEkey.- If a
DATA_UPDATEkey is present, the user's data will be set from the snapshot deserialized from Redis contained within that key. - Otherwise, their data will be pulled from the database.
- If a
- When a user disconnects from a server, their data is serialized and set to Redis with a
DATA_UPDATEkey. After this key has been set, the user's currentDATA_CHECKOUTkey will be removed from Redis.
Additionally, note that DATA_CHECKOUT keys are set with the server ID of the server which "checked out" the data (taken from the server.yml config file). On both shutdown and startup, the plugin will clear all DATA_CHECKOUT keys for the current server ID (to prevent stale keys in the event of a server crash for instance)
Delay
The DELAY sync mode works as described below:
- When a user disconnects from a server, a
SERVER_SWITCHkey is immediately set on Redis, followed by aDATA_UPDATEkey which contains the user's packed and serialized Data Snapshot. - When the user connects to a server, they are marked as locked (unable to break blocks, use containers, etc.)
- The server asynchronously waits for the
network_latency_milisecondsvalue (default: 500ms) to allow the source server time to serialize & set their key. - After waiting, the server checks for the
SERVER_SWITCHkey.- If present, it will continuously attempt to read for a
DATA_UPDATEkey; when read, their data will be set from the snapshot deserialized from Redis. - If not present, their data will be pulled from the database (as though they joined the network)
- If present, it will continuously attempt to read for a
DELAY has been the default sync mode since HuskSync v2.0. In HuskSync v3.1, LOCKSTEP was introduced. Since the delay mode has been tested and deployed for the longest, it is still the default, though note this may change in the future.
However, if your network has a fluctuating tick rate or significant latency (especially if you have servers on different hardware/locations), you may wish to use LOCKSTEP instead for a more reliable sync system.